Irrigation systems are vital to modern agriculture, enabling farmers to effectively manage water resources and enhance crop yields, especially in regions with unpredictable rainfall or arid climates. The use of various irrigation technologies across the world has transformed farming practices, providing critical support in food production.
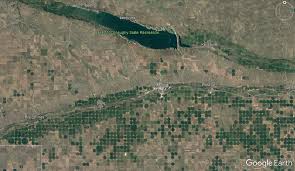
In the United States, pivot irrigation systems are among the most common methods employed, particularly in the Great Plains. These circular, mechanised systems allow for large expanses of crops to be watered efficiently, reliant on engines that rotate over a fixed pivot point. Pivot systems enhance water conservation techniques by minimising evaporation and runoff, demonstrating a commitment to sustainable agricultural practices amid growing concerns over water scarcity.
Across the Mediterranean region, where dry summers pose significant challenges for crop production, drip irrigation has gained popularity. This method delivers water directly to the plant’s roots through a network of tubes and emitters. Farmers in countries like Spain and Italy have adopted drip irrigation to maximise water efficiency, essential for cultivating high-value crops such as fruits and vegetables. The result is not only higher yields but also improved quality, allowing farmers to compete effectively in both local and international markets.
In Asia, particularly in countries like India, irrigation systems have been pivotal in boosting agricultural productivity. Smallholder farmers often utilise a combination of traditional and modern methods, including micro-irrigation technologies like drip and sprinkler systems. These systems have been promoted by government initiatives aimed at improving water conservation and increasing crop resilience to climate change. The adoption of small-scale, affordable irrigation technologies has empowered farmers, making it easier to increase food security across diverse regions.
In arid regions of Africa, innovations in irrigation technology are transforming agriculture. Countries like Kenya and South Africa have witnessed notable advancements in solar-powered irrigation systems. These systems enable farmers to harness renewable energy for pumping water, significantly reducing operational costs. By using solar energy, farmers can improve water access without the burden of expensive fuel costs, making irrigation more feasible and sustainable for rural communities.
Moreover, the increased focus on precision agriculture has enhanced the efficacy of irrigation practices. Utilising soil moisture sensors and weather forecasting technologies enables farmers to apply water only when necessary, promoting efficient water use. This shift not only conserves one of our most precious resources but also optimises crop growth, contributing to the overall sustainability of agricultural practices.
In conclusion, irrigation systems play a crucial role in modern agriculture, contributing significantly to food security and enhancing productivity across the globe. From pivot systems in the US to solar-powered solutions in Africa, the diversity of irrigation technologies showcases innovation in response to unique challenges faced by farmers. As climate change and water scarcity loom over agricultural landscapes, the continued evolution of irrigation methods will be essential in shaping the future of farming and ensuring sustainable practices worldwide.